Start-up of the reactor
Start-up of the reactor
In this guide, we will walk through the necessary steps from the beginning of the game to stabilizing the reactor, outlining the initial parameters and detailing what occurs internally during each stage.
The guide may be somewhat lengthy, but it is crucial to comprehend not only what actions to take, but also why they are necessary.
Initial parameters
Keep the default values that start a new game in place: the Condenser volume at the lower limit (beginning of the yellow zone).
Set the main circulation pump to 50% and wait for it to reach its nominal speed:
Start of reaction
To initiate the reaction, withdraw the control rods up to 95% and introduce the fuel into the reactor core. At that point, the game will indicate that the chain reaction has begun.
At this stage, the Evaporator's volume will begin to decrease, but it is not yet time to start the Condenser's circulation pumps. You should wait until the turbines begin to expel steam and the steam completes its journey to the condenser.
This may take several minutes to occur. In the meantime, the Evaporator will continue to generate steam and thus decrease its internal refrigerant level.
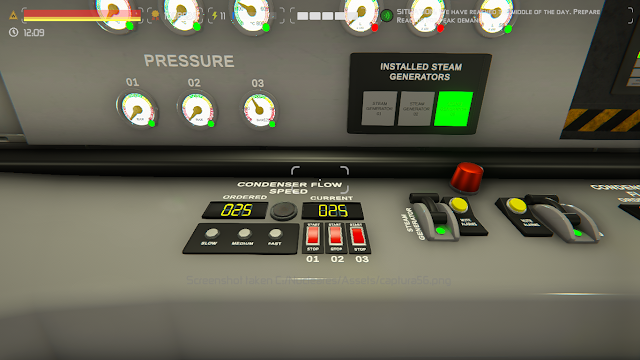
Condenser circulation pump on
Once the steam reaches the condenser, you will notice that the temperature begins to rise. At this stage, it is crucial to activate the condenser circulation pump at a low speed, no higher than 10%.
Condensed water would have cooled down excessively, since the condenser has just started receiving vapor, and when the pump propels that refrigerant back to the evaporator, it will cause the evaporator to also cool down.
At this point, the first peak of energy will have been reached, and the turbines will come to a stop.
Power increase
Now is the opportune moment to increase the power output. Pull the control rods up to 90% to raise the temperature of the core and offset the influx of still-cold water from the condenser.
Now the condenser is not cooling the refrigerant returning to the evaporator as effectively, resulting in all temperatures in the circuit rising evenly and steadily. The core, evaporator, turbines, and condenser will be in balance.
Checks on the Condenser
As the core power increases, the evaporator will generate higher vapor pressure, and the condenser will need to absorb more energy. It's crucial to prevent the condenser from getting too hot, as it may initiate an upward spiral that could ultimately lead to the circuit's complete loss of control.
Once the internal temperature of the condenser has reached between 80°C and 90°C, you should turn on the cooling pump at a very low speed, no more than 5% to start with.
If the internal temperature of the condenser continues to rise, you must increase the circulation speed until the temperature rise stops and even reverses slightly. At this stage, it should not exceed 10%.
At this point, it is crucial to monitor the internal volumes of the evaporator and the condenser: both should be in the green or yellow zone.
Condenser:
If Condenser or Evaporator are too full or too empty, the achieved balance will be lost, resulting in extreme fluctuations such as high temperature and pressure, and generator turbines experiencing exaggerated energy peaks followed by sudden drops to zero.
If the volumes, temperatures and pressures remain within the operating ranges, in a few minutes the reactor will have stabilized. At that time, the core temperature will have stopped increasing.
Power increase up to operating level
If you wish to increase the reactor's power output, you can slightly withdraw the control rods. It's recommended to do this gradually in increments of 5% or 10%, while waiting for the circuit to stabilize between each adjustment.
This approach ensures a safe and steady increase in power output.
After each power increase, check whether it is necessary to increase the speed of the condenser refrigeration pump (if the internal temperature has increased) or the speed of the condenser circulation pump (if the evaporator volume has decreased). Make gradual speed increases, around 5%.
Core
Do you have more questions? Need help?
We are waiting for you in the game's Discord!